Fruits and vegetables, foods rich in antioxidants
Fruits and vegetables are rich in fiber, vitamins and minerals, they are vital foods for our bodies and our best friends for health and vitality.
But what is the reason for such passion for fruits and vegetables?
Their secret: they are rich in antioxidants! And these antioxidants give fruits and vegetables an appetizing color. These known compounds defend the body against free radicals (FR) (destructive and potentially toxic molecules that damage our cells and biological molecules).
What are free radicals and how do they damage the body?
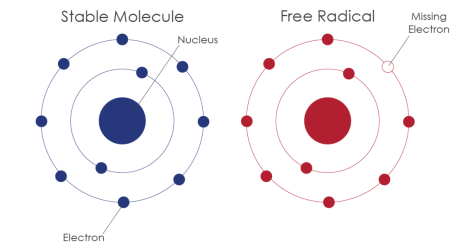
A free radical (FR) is an atom characterized by the presence of a single, unpaired electron, which makes it unstable and particularly aggressive to surrounding molecules.
In order to find its missing electron and become stable, the free radical "attacks" other atoms and takes the precious missing electron from the other atom. This atom loses an electron and becomes a free radical.
In this way, a chain of destructive reactions is created, which causes (often) irreversible damage to biological substrates such as enzymes, proteins, DNA, etc., and according to the theory of aging caused by free radicals that First proposed in 1956, free radicals break down cells over time...unless antioxidants are used.
As we age, the body loses its ability to fight the effects of free radicals. The result is more free radicals, more oxidative stress and more damage to cells, leading to degenerative processes as well as "natural" aging.
Various studies and theories have linked oxidative stress caused by free radicals to the following diseases and injuries:
Diseases of the central nervous system, such as Alzheimer's and other dementias
Cardiovascular disease caused by blood clots
Trusted Source Autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and cancer
Cataracts and age-related vision loss
Appearance changes associated with aging, such as loss of skin elasticity, wrinkles, gray hair, hair loss, and changes in hair texture.
diabetes
Degenerative genetic diseases, such as Huntington's or Parkinson's disease
Reasons:
Free radical theories of aging and disease may help explain why some people age more slowly than others.
Although free radicals are naturally produced in the body, lifestyle factors can accelerate their production. They are:
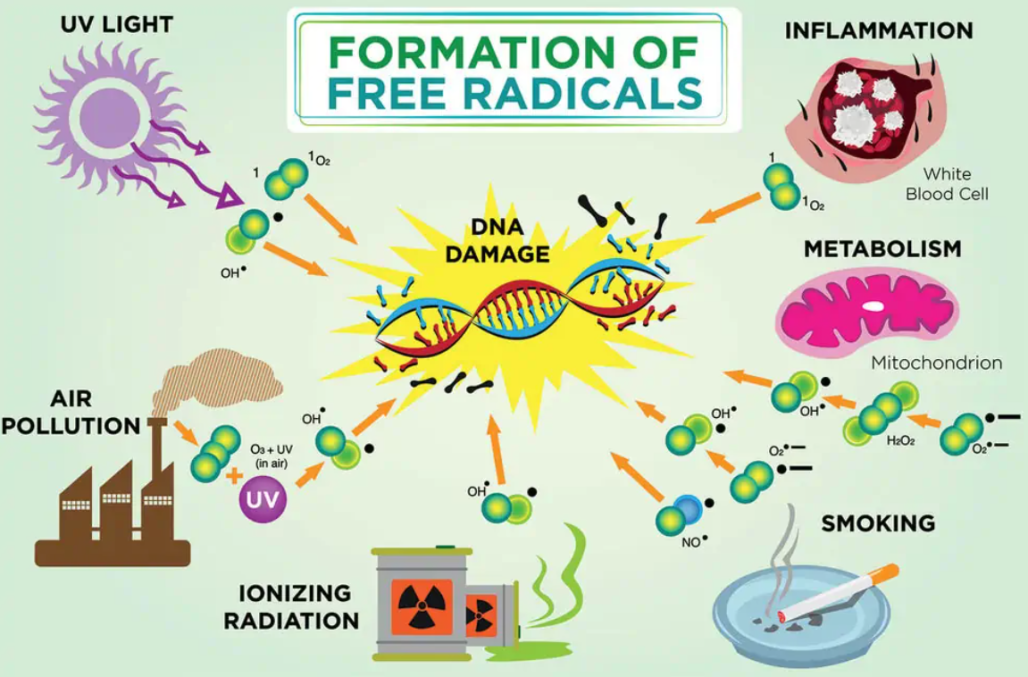
Exposure to toxic chemicals such as pesticides and air pollution
smoking
alcohol
Fried foods
These lifestyle factors are associated with diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular disease. Therefore, oxidative stress may be the reason why exposure to these substances causes disease.
Our environment is also a source of free radicals:
When exposed to too much sunlight
When exposed to electromagnetic radiation, pollution, pesticides, etc.
However, the formation and use of free radicals can be of vital importance to the body: this is the case during the process of antibacterial defense, gene regulation and cell destruction.
Excess free radicals and oxidative stress
Fortunately, the body has its own defense systems:
Internal: enzymes, proteins and trace elements such as copper, zinc and selenium
External: through diet, especially fruits and vegetables
But if the production of free radicals exceeds the neutralization capacity of the body, it causes oxidative stress, for example in the following cases:
If the diet lacks antioxidant nutrients or is too unbalanced due to sugar, fat, etc., which is often the case in industrialized societies.
In times of chronic stress, which often exists in the modern world, these prolonged stresses are recognized as a real enemy in terms of nutrient and antioxidant consumption.
In case of frequent or high exposure to chemical pollutants or UV or electromagnetic radiation
During intense endurance exercise
during chronic or acute inflammatory phenomena
Antioxidant, very effective against free radicals
We group them under the name "antioxidants"—molecules that help protect our bodies from free radicals. Compounds known as "regenerators" can interact with an "oxidant" free radical and neutralize it by donating an electron to make it stable.
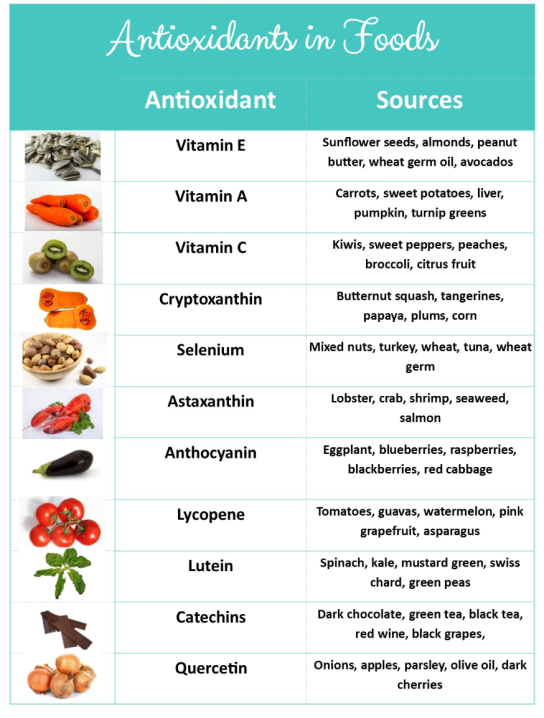
There are many natural antioxidants that include:
Vitamin E is certainly the most well-known antioxidant that plays an important role in protecting cell membranes.
Vitamin C, an essential nutrient for the body
Vitamin A as well as carotenoids that can be converted to vitamin A
Minerals such as zinc and selenium
Flavonoids are a family of polyphenolic compounds found in most fruits and vegetables.
The colors in your meal fight oxidative stress!
If fruits and vegetables have such a variety of colors, it is because, in addition to antioxidant vitamins and trace elements, they contain pigments with a high anti-radical effect. The darker the color, the higher the anti-radical effect. The greater the range of colors in the meal, the wider the range of antioxidants, which is an important factor because they work synergistically to neutralize a variety of free radicals.
A few antioxidants to add to your plate:
Causes and Consequences
of an excess of free radicals
The formatin
of free radicals

